GHANAIAN AGRICULTURE FOOD LANDSCAPE
Ghana has a population of 25.37 million, with a per
annum growth rate of 2.19%, and a mean population
density of 77 persons/km2. The population distribution
is varied across the 10 administrative regions and
eco-zones of the country, with 68% and 32% living in the
rural and urban areas respectively. About 52% of the
labour force is engaged in agriculture, 29% in services
and 19% in industry. Approximately, 39% of farm labour
force is women. Agriculture contributes to 21% of
Ghana’s GDP, and accounts for over 40% of export
earnings, while at the same time providing over 90% of
the food needs of the country.
About 136,000 km2 of land, covering approximately 57%
of the country’s total land area of 238,539 km2 is
classified as "agricultural land area" out of which 58,000
km2 (24.4%)is under cultivation and 11,000 hectares
under irrigation.
Despite being agriculture-centric, Ghana is not able to
cater to its own domestic demands and has to import
large number of crops to satisfy its domestic needs.
Cereals crops are the most imported commodity in
Ghana, and among them, rice and wheat are the
leading imports.
FOOD CROP PRODUCTION
-
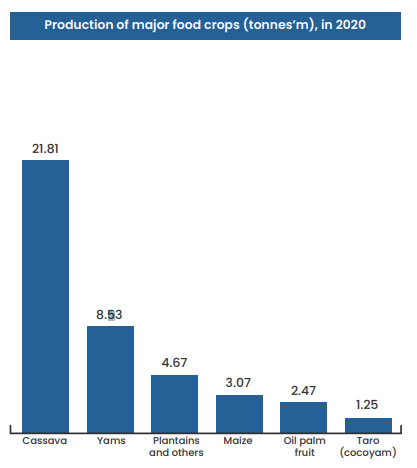
With production of 22m tonnes in 2020. Ghana is
the fourth largest producer of cassava in the world.
-
Cassava is a very important root crop in Ghana with
an estimated land area of 1 million hectares being
used for cassava prodcution and about 70% of
farmers in Ghana are into cassava production.
-
Ghana is the second largest producer of yam in
the world behind Nigeria having produced 8.5
million tonnes in 2020. The variety of yam produced
in Ghana include pona, larebako, asana, dente, and
muchumudu. The unique taste and quality of the
pona variety is most preferred by consumers.
-
Ghana also produces large quantities of plantain,
maize, rice paddy, oil palm, oranges, pineapples,
groundnuts, and coconuts.
GHANA GRAIN & CEREAL IMPORTATION
-
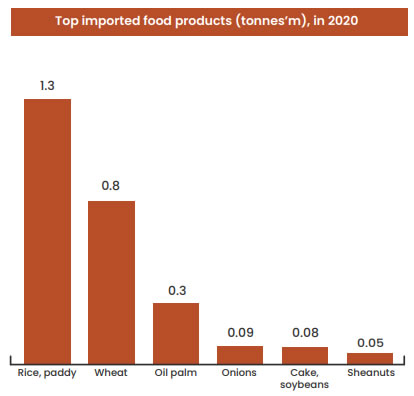
Ghana imports a large amount of rice paddy on an
annual basis; 1.3 million tonnes of paddy rice was
imported in 2020 as compared to 1 million tonnes
produced locally. Aside paddy rice, a significant
amount of internationally produced milled rice is
imported to supplement locl supply.
-
Aside rice, Ghana imports other cereals into the
country. Imported cereals in 2020 include wheat
(873,000 tonnes), soybeans (84,333 tonnes),
shea nuts (49,963 tonnes), malt (22,312 tonnes).
-
Fruits and vegetables imported into the country in
2020 include apples (11,160 tonnes), garlic (7,081
tonnes), and tomatoes (4,000 tonnes).
LIVESTOCK AND GAME PRODUCTION
-
The Rearing for Food and Jobs (RFJ) module of the
flagship agriculture sector policy initiative, Planting
for Food and Jobs, was launched in 2019. The
initiative contributed the growth in the production of
livestock in 2020.
-
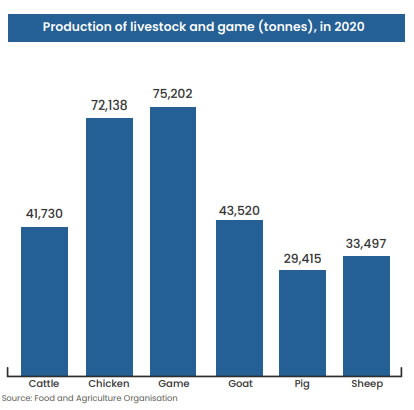
In 2020, production increased by 3%, 6%, 5%, and 4%
for cattle, chicken, goat and sheep meat,
respectively.
-
Chicken, one of the largest sources of livestock
protein in Ghana, and game led the way in the
production of meat recording 72,138 tonnes and
75,202 tonnes respectively.
IMPORTATION OF LIVESTOCK AND GAME
-
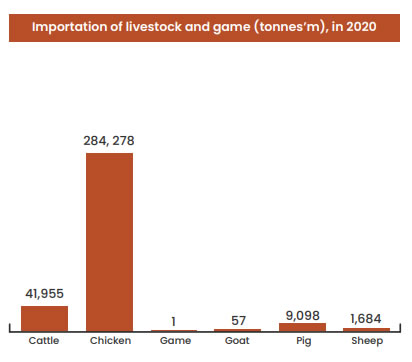
Chicken formed about 84% of the total meat mports
in 2020; chicken import was more than 500% of the
combined imports of cattle, game, pig, and
sheep meat.
-
Chicken importation was almost 4 times of the
domestic production in 2020.
-
In 2020, Ghana also imported 25,000 tonnes and
10,000 tonnes of cattle offal and beef & veal
respectively to supplement local production
of cattle.
IRRIGATION IN GHANA
-
Ghana’s agriculture sector is dominated by small scale, traditional, and rain dependent farmers.
-
In 2017, the government of Ghana initiated the “One Village One Dam Policy” to reduce the sole reliance
on rainfall and allow for year round farming across the country.
-
As of 2021, 507 small earth dams out of the 560 targeted, under the One Village One Dam” had been
completed. The government is also in the process of riprapping the upstream slopes of completed
dams to increase the lifespan and safety of the dams.
-
Significant investments have also been made to rehabilitate and revamp major irrigation schemes
including the Tono , Kpong Irrigation Scheme and the Kpong Left Bank Irrigation Project (KLBIP) which
were at 93%, 97%, and 90% completion rate respectively as of September 2021.
-
KLBIP is located on the left bank of the Volta River downstream of the Kpong Hydroelectric Dam at Akuse
and is expected to provide 2,100 ha of irrigation area.
WAREHOUSING
-
Lack of storage facilities in the past has contributed to significant post harvest losses in Ghana.
-
Government has taken a plethora of initiatives to increase warehousing capacity in the country. In 2016,
a public private partnership funded the establishment of the Ghana Airport Cargo Centre at the Kotoka
International Airport; the facility has a capacity of 10,000 m2.
-
In 2018, the erstwhile Ministry of Special Initiative in its Medium Term Expenditure Framework (MTEF)
committed to constructing 50 prefabricated grain warehouses; each with a capacity of 1,000 metric
tonnes . 42 out of these 50 warehouses were completed as of December 2020.
-
The Government of Ghana has also launched the “0ne District One Warehouse” intervention to increase
storage capacity. As of September 2021, 23 warehouses, each with a capacity of 1,000 metric tonnes ,
had been completed out of the target of 30.